

The compression of the sac below this level may result in loss of bowel bladder control, numbness of the saddle area. Patients may also experience weakness of the legs or feet.Ĭauda equina syndrome results from compression of the nerve roots from a large central disk herniation below the L1-L2 vertebrae. Some patients may complain of numbness and tingling of the feet or legs. The patients may also experience shooting pains in the buttocks radiating to the back of the legs and feet.
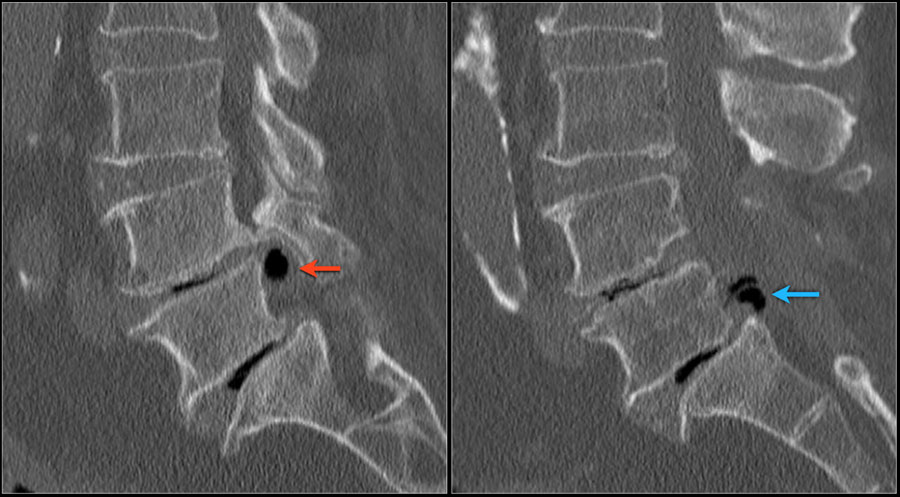
In the lower back, a herniated disk commonly results in pain of the lower back. The symptoms of a herniated disk depend on the location of the herniation and the amount of compression on the neural structures. Lifting weights and traumatic injuries frequently result in PIVD. Obesity, smoking, and improper posture while sitting or standing to make the disks more vulnerable to injuries resulting in PIVD. Repetitive activities such as bending, turning, twisting may cause tears in the annulus. The prolapsed intervertebral disk is more common in adults aged 30 and more as with age the nucleus pulposus starts losing the water content, making it more susceptible to injuries. The herniated disk in the majority of the cases occur in the lower back (lumbar spine) and the rest of the cases involve the neck (cervical spine). The sinuvertebral nerve arises from the dorsal root ganglion and supplies the most superficial layer of the annulus fibrosis.Īxial section of the spine showing central disc herniation. The nucleus pulposus has a watery gel-like consistency giving it the ability to resist compression and allow cushioning action. The annulus fibrosis consists of concentric layers of thick fibers which imparts it the property of elasticity while being tough. The endplate is thick in childhood and gradually decreases in thickness. The endplate is formed by cartilage that contributes to the growth of the vertebra. The outer layer adjoining the vertebrae is known as the endplate. The intervertebral disks consist of a thick fibrous outer layer known as the annulus and a soft center known as the nucleus pulposus. The disk acts as a cushion between two vertebrae and provides stability. The intervertebral disk is a disc-shaped circular tissue present between the adjacent vertebrae. The herniated disk also known as the prolapsed intervertebral disk is a condition affecting the spine frequently causing neck pain or back pain.

If you suspect you may have PIVD, it’s important to seek medical attention to determine the best course of action for your specific case. Treatment options range from conservative measures like rest and physical therapy to more invasive procedures like surgery. PIVD can be caused by age-related wear and tear, injury, or degenerative conditions. This can cause pain, numbness, weakness, and other symptoms. That test may also reveal the herniated disc in great detail.PIVD, or Prolapsed Intervertebral Disc, is a condition that occurs when the material inside a spinal disc bulges or ruptures through the outer layer and compresses the nerves in the spinal canal. Another less used test is the CT myelogram of the cervical spine. Usually the MRI will not be done unless you have had symptoms for several weeks. The MRI is best for evaluating the soft tissue in the spine and neck and is therefore the best way to find the slipped disk. Is the CT scan better than the MRI for diagnosing an herniated disc?– No. The CT is very good to check for fracture. CT scans also look at bones and use x-rays but takes very thin slices of the bone and is more detailed than a plain x-ray. A neck or cervical x-ray can reveal a fracture, tumor, arthritis or instability. The MRI is most sensitive and will usually be ordered if you have persistent neck pain with pain radiating down the arm, with arm numbness and tingling or weakness. To see the disc you must obtain a CT scan or MRI. Seth Neubardt, cervical spine surgical expert tells how the x-ray is used to check the bones in the neck but it cannot reveal a herniated disc.
BACK BULGING DISK XRAY FULL
What’s The Difference Between An X-Ray, CT Scan and MRI? Which Is Best For Herniated Disc?Ĭlick here to download a full video transcript.ĭo I need an x-ray, CT scan or MRI to diagnose the herniated disc in my neck? Which is best for a herniated cervical disc? What’s the difference between the x-ray, CT and MRI scan? Dr.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
